Inflation Relief: Food Prices Decline, but Challenges Persist
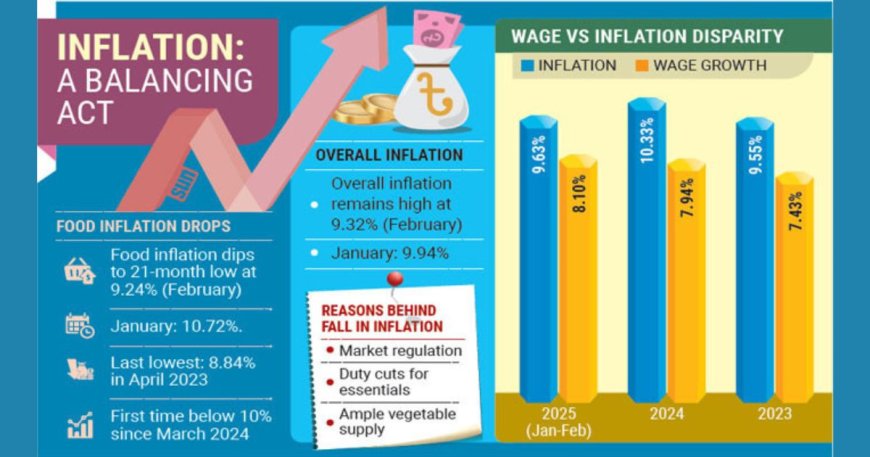
The food inflation rate in February stood at 9.24%, marking a notable decrease from 10.72% in the previous month.
Inflation Relief: Food Prices Decline, but Challenges Persist
-
Food Inflation at 21-Month Low
- In February, food inflation dropped to a 21-month low, offering slight relief to consumers.
- The overall inflation rate also declined compared to the previous month, as per the Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS).
-
Government Measures and Economic Impact
- Interim government initiatives, including market regulations, reduced import duties on essentials, and increased interest rates, have played a role in curbing inflation.
- Experts note that while food prices have eased, high non-food inflation and stagnant wages continue to burden households.
-
Inflation Trends and Current Rates
- February food inflation was 9.24%, down from 10.72% in January—the lowest since March 2024.
- The overall inflation rate also fell to 9.32% in February from 9.94% in January, yet remains above a comfortable level for many.
- This marks the second time in four months that inflation has returned to single digits, providing some optimism amid financial strain.
Factors Behind Food Price Decline
- Seasonal reductions in winter vegetable prices and a stable rice market contributed to the drop.
- Government interventions, such as lowering import duties on essentials like oil, onions, and eggs, helped stabilize food costs.
Persistent Challenges: Non-Food Inflation & Wage Gap
-
Non-Food Inflation:
- Increased slightly to 9.38% in February from 9.32% in January.
- Expenses on housing, transportation, and healthcare continue to exert financial pressure on households.
-
Wage vs. Inflation Disparity:
- Inflation has consistently outpaced wage growth over the past three years.
- In 2024, inflation averaged 10.33%, while wage growth was only 7.94%.
- The purchasing power of low-income families has declined, intensifying financial struggles.
Government Response & Future Outlook
-
Current Measures:
- Interest rate hikes to control excess demand.
- Tax reductions on key goods to ease consumer burdens.
- Efforts to stabilize prices, especially during Ramadan.
-
Expert Insights & Forecasts:
- Economists stress the need for consistent policies to ensure long-term market stability.
- The government aims to reduce inflation to 6-7% by June 2025.
- External factors like global economic conditions, fuel prices, and climate disruptions could impact future price stability.
Impact on Everyday Lives
- Many families, especially in lower-income groups, continue to struggle with the rising cost of living.
- Wage stagnation, coupled with inflation, forces families to cut essential expenses, including education and healthcare.
Employment & Economic Growth
- Finance Advisor Dr. Salehuddin Ahmed emphasized the need for job creation to address economic challenges.
- Plans to boost business activities and support SMEs could help mitigate financial pressures in the long run.
Conclusion
While the decline in food inflation provides some relief, Bangladesh still faces significant economic hurdles. The government’s measures will be closely monitored, as the long-term solution lies in sustainable economic growth, wage adjustments, and structural reforms to control inflation effectively.
What's Your Reaction?