What Is the F-7 BGI Fighter Jet? Its Capabilities, Origins, and Role in Bangladesh Air Force
What Is the F-7 BGI Fighter Jet? Its Capabilities, Origins, and Role in Bangladesh Air Force
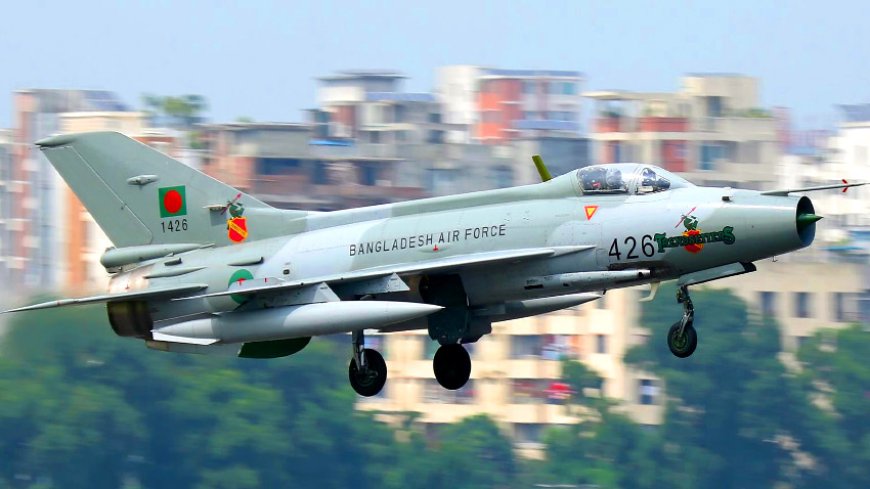

The F-7 BGI is a Chinese-built fighter jet and an advanced version of the F-7 series, which traces its design lineage to the Soviet-era MiG-21. Known as the Chengdu J-7 in China, this single-engine, lightweight interceptor was originally developed for the People’s Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF) and has since been adopted by several countries, including Bangladesh. Its delta-wing design enables high-speed ascents and supersonic flight, making it effective in short-range interception roles.
Bangladesh has operated F-7 variants for decades, with the F-7 BGI being the most sophisticated model in its fleet. Customized specifically for the Bangladesh Air Force (BAF), the BGI was acquired as a stopgap measure until more modern, multirole aircraft could be introduced. It serves multiple roles, including air-to-air combat, ground attack, surveillance, patrol, and pilot training.
Compared to earlier models, the F-7 BGI features several modern upgrades: a glass cockpit with dual multifunction displays (MFDs), Hands-On Throttle and Stick (HOTAS) controls, an advanced head-up display (HUD), helmet-mounted sight (HMS) with night vision compatibility, moving map GPS, and an integrated navigation and bombing system. It is also equipped with a Martin-Baker Mk.10 ejection seat to enhance pilot safety.
Although the final F-7 BGI units were delivered in 2013—marking the end of J-7 production—the aircraft remains active in Bangladesh's fleet. While its limited range and aging design restrict it to point-defense missions and training, the F-7 BGI has played a critical transitional role in Bangladesh’s air defense strategy and pilot development.
What's Your Reaction?